Actions
Shearing
Shearing is a cutting process that involves applying force through a slide or knife to trim or cut metal or other materials along a straight line. It is commonly used in metal fabrication to size large sheets or remove unwanted sections of material.
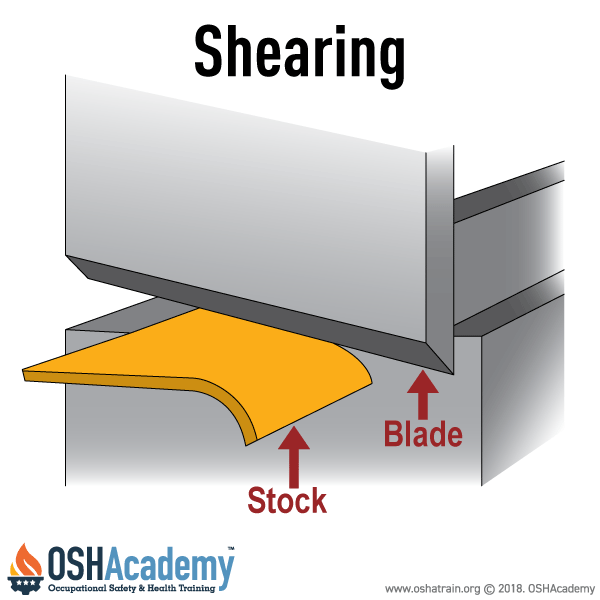
The image shows a machine shearing action, highlighting the point of operation where material is inserted and cut by the moving blade.
Key Features of Shearing Actions
The key features of shearing actions include the following:
- Involve a blade moving past a fixed edge to slice through material
- Produces straight-line cuts in metal, plastic, or other sheet materials
- Requires precise hand positioning to feed and align stock
- Is often powered by mechanical, hydraulic, or pneumatic systems
- Can cause severe lacerations, amputations, and crushing injuries
Examples
- Mechanically Powered Shears: These use gears and linkages to drive a blade through material. For example, a sheet metal shop may use this type of shear to cut roofing panels. If the operator's hand is too close, the quick downward stroke can cause instant injury.
- Hydraulically Powered Shears: These apply steady force using hydraulic pressure. They are ideal for cutting thick or heavy materials like steel plates. Even though the movement is slower, the high pressure can still cause significant harm if an operator tries to adjust the stock while the machine is running.
- Pneumatically Powered Shears: These use compressed air for quick, high-speed cutting. For instance, in an electronics assembly line, pneumatic shears may be used to trim metal cases. Their speed increases the chance of an accident if an operator attempts to reach into the cutting area without fully stopping the machine.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
1-9. What is the purpose of shearing in machinery?
You forgot to answer the question!
