Personal Protective Equipment
If other hazard and exposure control strategies to reduce noise levels can't be used or fail to reduce noise levels below OSHA's permissible exposure limits (PELs), the employer should make sure all exposed employees wear hearing protective devices.
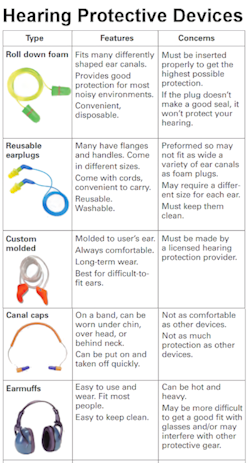
As you are probably well aware, there are basically four types of hearing protectors.
- Molded earplugs are usually made of plastic or silicone rubber. They are available in a variety of shapes and sizes and are usually characterized by one or more ribs or contours. They are considered multiple use; therefore, they must be cleaned and properly stored after each use.
- Custom-molded plugs are generally made of plastic and are designed from a molded wax insert of the wearer's ears. They are considered multiple use but cannot be switched ear to ear.
- Self-molded earplugs are generally made of mineral down or plastic foam and are molded or formed by the wearer. Generally one size fits all and they may be either single or multiple use.
- Earmuffs are designed to be multiple use and may be designed to be worn with the harness over or behind the head, or below the chin. They are generally more comfortable, but may not provide as much protection because they only sit over the ears, rather than directly in the ear canal.
Each type is designed for certain noise conditions. But remember - unless employees wear hearing protection properly and wear them all the time in high noise areas, the devices will not be effective. Proper use of hearing protection as required is one of the most common challenges inherent in this exposure control strategy.
Convenience and comfort are important for frequent use of hearing protective devices. Earmuffs and foam earplugs in most cases offer the most noise reduction. However, preformed plugs or canal caps may be more convenient where construction work generates moderate daily average noise levels. There is no one device that is the best type for all situations. You can see the various types by enlarging the image on this page.
We'll discuss the OSHA requirements for hearing protective devices as part of the employer's Hearing Conservation Program (HCP) later in the course.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
3-7. Which hearing protectors are generally most comfortable, but may not provide as much protection from noise?
You forgot to answer the question!