Administrative/Work Practice Controls
Administrative/Work Practice Controls are changes in policies, procedures, tasks, and work practices that mitigate worker exposure to noise. Examples include:
- Operating noisy machines during shifts when fewer people are exposed.
- Limiting the amount of time a person spends near a noise source.
- Providing quiet areas where workers can gain relief from hazardous noise sources (e.g., construct a soundproof room where workers' hearing can recover - depending upon their individual noise level and duration of exposure, and time spent in the quiet area).
- Restricting worker presence to a suitable distance away from noisy equipment. Controlling noise exposure through distance is often an effective, yet simple and inexpensive administrative control.
Controlling Noise Exposure With Distance
Restricting worker presence may be applicable when workers are present but are not actually working with a noise source or equipment.
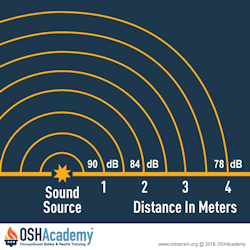
Increasing the distance between the noise source and the worker, reduces their exposure.
In open space, for every doubling of the distance between the source of noise and the worker, the sound level of the noise is decreased by 6.02 dB. No matter what the scale of measurement, you will get a 6.02 dB sound level drop for every doubling of distance.
Click on the link below to can see how this works by entering values in the table below.
Calculating Sound Levels With Changes in Distance
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
3-6. Which work practice control can reduce the risk of excessive noise exposure?
You forgot to answer the question!