Explosive/Flammability Limits
Lower Explosive/Flammability Limits (LEL/LFL)
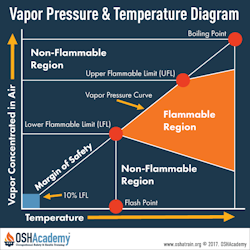
The lower explosive limit, or LEL, is the lowest concentration of a gas or vapor at which combustion can occur.
The lower flammability limit, or LFL, is the lowest concentration of a gas or vapor at which a flame can be sustained.
Concentrations below the LEL or LFL will not explode or burn because it has too little fuel and is considered too "lean."
Upper Explosive/Flammability Limits (UEL/UFL)
The upper explosive limit, or UEL, is the highest concentration of a gas or vapor that can support combustion.
The upper flammability limit, or UFL, is the highest concentration at which a flame can be sustained.
Concentrations above the UEL or UFL will not explode or burn because it has too much fuel and is considered too "rich."
Flammable Range
Gases or vapors can only be explosive or flammable between their LEL/LFL and UEL/UFL. This is called the explosive/flammable range.
The diagram above shows the relationship among the lower and upper explosive/flammability limits, explosive/flammable and non-explosive/flammable regions, flash points, and the vapor pressure curve. It also reveals what happens to a vapor/air mixture as concentrations and temperatures vary.
Substances with a wide explosive/flammable range are considered to be more hazardous since they are readily ignitable over a wider range. However, any concentration of combustible gas or vapor should be of serious concern in a confined space.
Workers should be especially careful when ventilating a space containing a gas or vapor above its UEL/UFL. In order to reduce the concentration below the LEL, this procedure will first bring the gas or vapor within its explosive/flammable range. When it does, the possibility of an explosion or fire exists.
The composition of a fuel vapor and air mixture can change over time and may fluctuate within a confined space. Fluctuations occur because the fuel-air mixture moves around the space, particularly when people or other things create air currents that disturb the atmosphere. Consequently, the mixture is not uniformly distributed within the space.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
4-5. Gases or vapors can only be explosive or flammable _____.
You forgot to answer the question!