Specific Bloodborne Pathogens
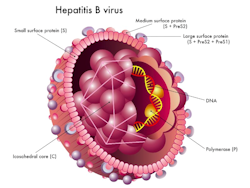
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
The hepatitis B virus (HBV) is one of the primary causes of hepatitis, an infection which causes inflammation of the liver. Complications of hepatitis include cirrhosis (scarring) of the liver, liver cancer, and liver failure. There is no known cure for the Hepatitis B virus.
Between 880,000 to 1.89 million people are living with HBV infection in the United States; two-thirds of whom may be unaware of their infection.
The Center for Disease Control (CDC) reported 3,322 confirmed acute cases and 21,600 estimate infections of hepatitis B in 2018. In the same year, a total of 1,649 US death certificates had HBV recorded as an underlying or contributing cause of death.
Hepatitis B can be either acute or chronic.
- Acute hepatitis B virus infection is a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to the hepatitis B virus. Acute infection can, but does not always, lead to chronic infection.
- Chronic hepatitis B virus infection is a long-term illness that occurs when the Hepatitis B virus remains in a person's body. Chronic hepatitis B is a serious
disease that can result in long-term health problems, and
even death.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
2-1. What describes a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after exposure to the hepatitis B virus?
You forgot to answer the question!